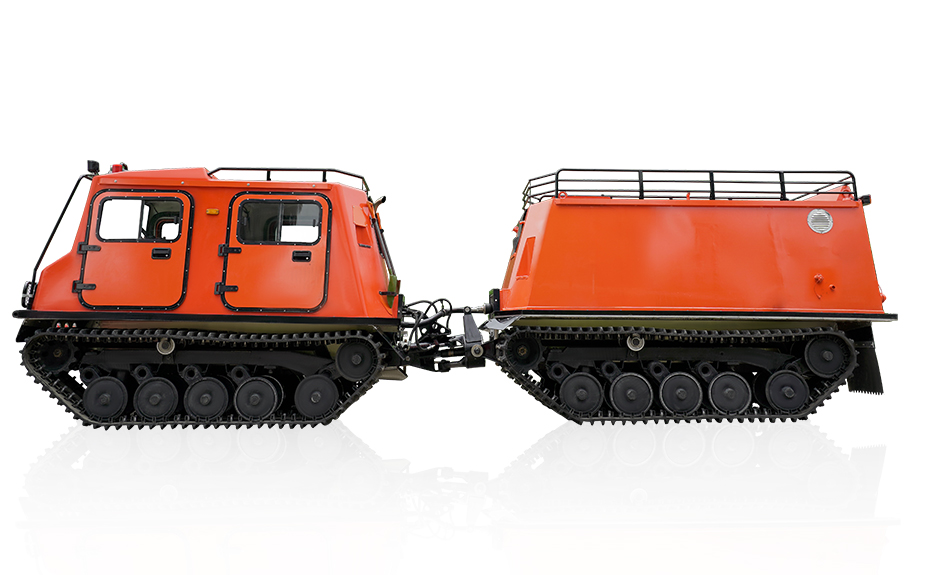

Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers Change Emergency Rescue Operations
In the ever-evolving world of emergency response, Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers (RTUTVCs) are becoming indispensable assets for responders. As natural disasters, remote rescues, and harsh weather events become more frequent, these versatile machines are redefining what’s possible in crisis scenarios. Their ability to traverse rugged, flooded, snowy, or debris-filled environments makes them an innovator for emergency rescue teams around the globe.
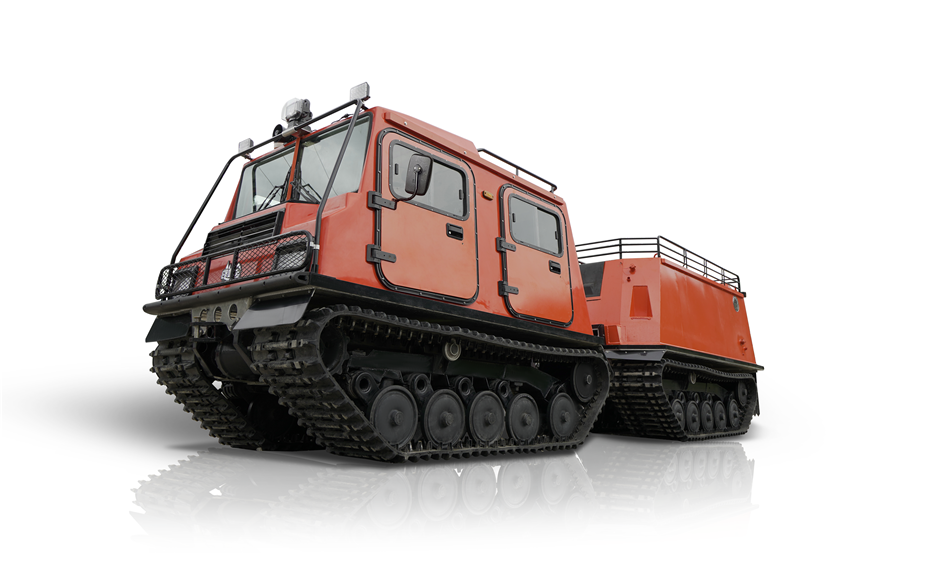
At their core, Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers are engineered for off-road mobility with little environmental impact. Unlike traditional wheeled rescue vehicles, these carriers use wide, rubberized tracks that distribute weight evenly across challenging terrain. This gives them a critical advantage in situations like wildfires, floods, landslides, or remote mountain rescues, where traditional vehicles may fail.
In recent months, several emergency situations have showcased the good capabilities of Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers. During the March 2025 flood in Northern California, local emergency teams deployed a fleet of RTUTVCs to rescue over 150 people stranded in areas inaccessible by boat or air. Their amphibious capabilities and low ground pressure allowed them to move across submerged roads and marshy terrain with ease.
"Without the Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers, we would have lost precious hours navigating washed-out roads and unstable ground,” said Captain Elias Morgan of the Sacramento Emergency Task Force. “These carriers made the difference between life and death in several rescue scenarios.”
A growing number of emergency management agencies across North America, Europe, and Asia are integrating RTUTVCs into their rapid response toolkits. Their modular design is particularly appealing. Carriers can be quickly configured to transport medical teams, carry stretchers, or haul emergency supplies, all while keeping operators and patients safe from harsh environmental conditions.

Manufacturers of Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers report a sharp increase in demand, driven in part by climate-related emergencies and greater investments in disaster preparedness. “We’ve seen a 35% year-over-year rise in orders from emergency response agencies,” said Vanessa Liu, senior product manager at TrailTek Industries, a RTUTVC manufacturer. “Agencies are realizing that conventional vehicles just aren’t cutting it anymore. Our carriers offer a scalable, reliable solution.”
One good feature of modern Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers is their ability to operate in extremely cold climates, where traditional diesel engines often fail. In Canada’s Yukon Territory, search and rescue teams recently used RTUTVCs to reach a group of stranded snowmobilers in -40°C conditions. The vehicles were equipped with insulated cabins, GPS navigation, and autonomous driving assist—all crucial features in harsh, isolated environments.
Another advantage lies in the durability and ease of maintenance of the rubber tracks themselves. Unlike steel tracks, which can damage roads and require more upkeep, the rubberized versions are more adaptable and resilient. This allows Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers to be used for both emergency and logistical missions, reducing the overall cost of operation.
As urbanization pushes development into more disaster-prone regions, municipal governments are also exploring RTUTVCs as part of community emergency planning. Pilot programs in Japan and the Philippines are using Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers to pre-position resources in remote or hard-to-reach areas before typhoon season.
Looking forward, technological advancements are set to further enhance the capabilities of Rubber Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle Carriers. Electric powertrains, autonomous navigation, and AI-driven obstacle detection are currently being tested by several manufacturers. These innovations aim to reduce environmental impact while increasing the carriers' reliability in high-risk environments.













 浙ICP备2022029871号
浙ICP备2022029871号