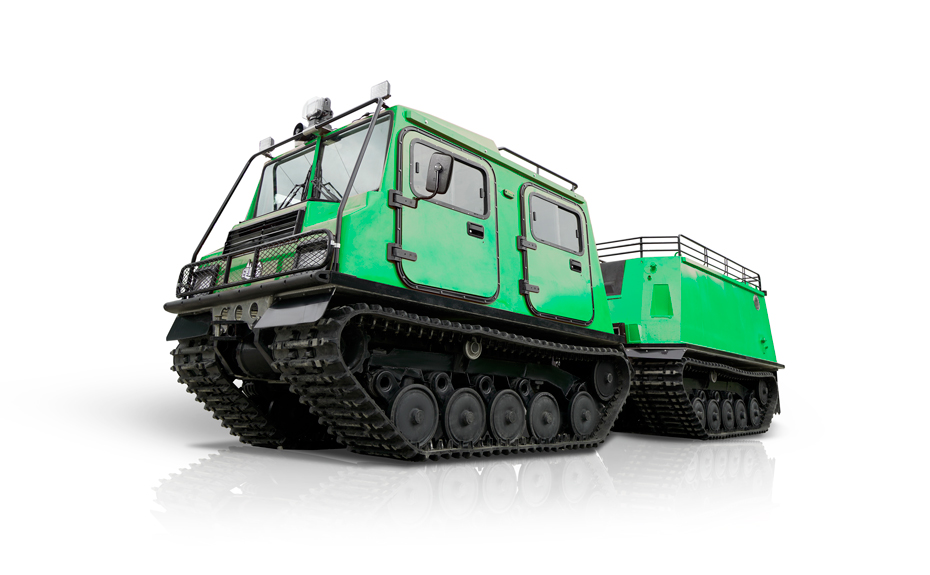

Tracked Carrier Applications and Advantages
Across construction sites, agricultural fields, and remote energy projects, a specialized class of vehicle is proving indispensable for material transport where conventional wheeled trucks falter. This machine, known universally as the tracked carrier, is a rugged, go-anywhere workhorse engineered not for speed, but for stability, traction, and access in the many challenging environments. The modern tracked carrier has evolved from a simple military concept into a sophisticated industrial tool, defined by its unique set of mechanical advantages, diverse power and capacity configurations, and its critical role in sectors where ground conditions are unpredictable and reliability is paramount.
What Are the Core Advantages of a Tracked Carrier?
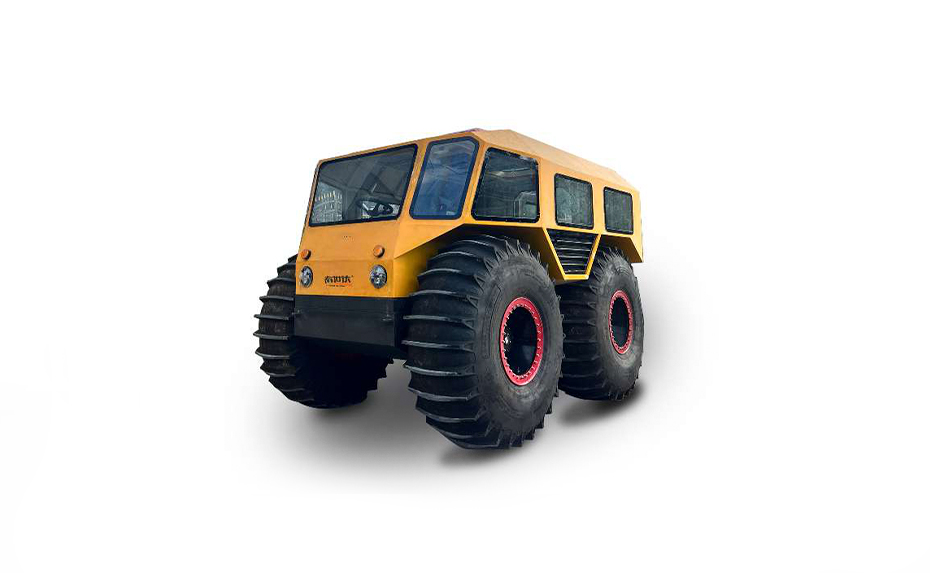
The defining strength of a tracked carrier lies in its fundamental design. By distributing the vehicle's weight over a large contact area via its rubber or steel tracks, the tracked carrier exerts significantly lower ground pressure than an equivalent wheeled vehicle. This engineering principle allows it to traverse soft, muddy, or uneven terrain—from saturated construction sites to snow-covered fields—with remarkable stability and small risk of becoming stuck or causing excessive ground disturbance. This low-impact characteristic is highly valued in agriculture, where soil compaction can reduce crop yields, and in environmentally sensitive work areas. Furthermore, the continuous track system provides exceptional traction and climbing ability, enabling a tracked carrier to navigate steep inclines and declines that would be hazardous or impossible for standard trucks, directly translating to expanded operational access and safety on job sites.

What Powers a Tracked Carrier and What Are Its Key Specifications?
The tracked carrier market offers a wide spectrum of models tailored to specific duty requirements, primarily distinguished by their power source and load capacity. Diesel engines remain a prevalent choice for heavy-duty applications, providing high torque and endurance for long shifts in remote locations. Increasingly, electric and hybrid-powered tracked carrier models are emerging, offering quieter operation and zero on-site emissions for indoor or environmentally regulated projects. In terms of capability, tracked carrier units are available in sizes ranging from compact utility models with payloads under one ton, designed for maneuvering in confined spaces, to large-scale haulers capable of carrying loads of six tons or more. This scalability ensures that whether the task involves moving bulk gravel on a mining site or delicate seedlings in a nursery, there is a tracked carrier specification engineered to match the demand efficiently.
Where Are Tracked Carriers Primarily Applied?
While a common sight in building and demolition, the utility of the tracked carrier extends far beyond traditional construction. In the agricultural and forestry sectors, these vehicles are used to transport harvested crops, feed, timber, and equipment across wet, uneven, or hilly terrain without damaging the underlying soil structure. The energy sector, particularly oil and gas exploration and renewable energy installation, relies on tracked carrier platforms to deliver personnel and heavy components to remote, unprepared sites where building a road is impractical. Furthermore, municipalities and environmental contractors utilize tracked carriers for waste management in landfills and for restoration projects in marshy or delicate ecosystems. This broad industry adoption underscores the tracked carrier's role as a fundamental enabling technology for operations that must proceed regardless of ground conditions.
The tracked carrier has cemented its position as a critical piece of mobile infrastructure in industries that operate at the frontier of accessible terrain. Its value is not measured in speed but in dependable access and small environmental footprint. As industries continue to push into more challenging environments and place a higher premium on sustainable operation, the design principles of the tracked carrier—emphasizing low ground pressure, adaptable power, and rugged durability—are likely to see even wider application and technological refinement, ensuring its continued relevance in building and maintaining the modern world.
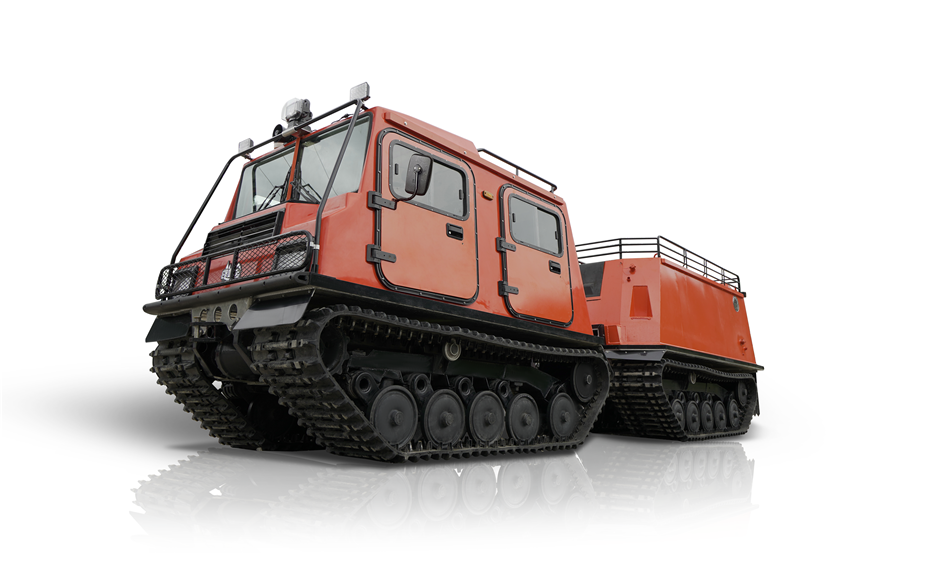
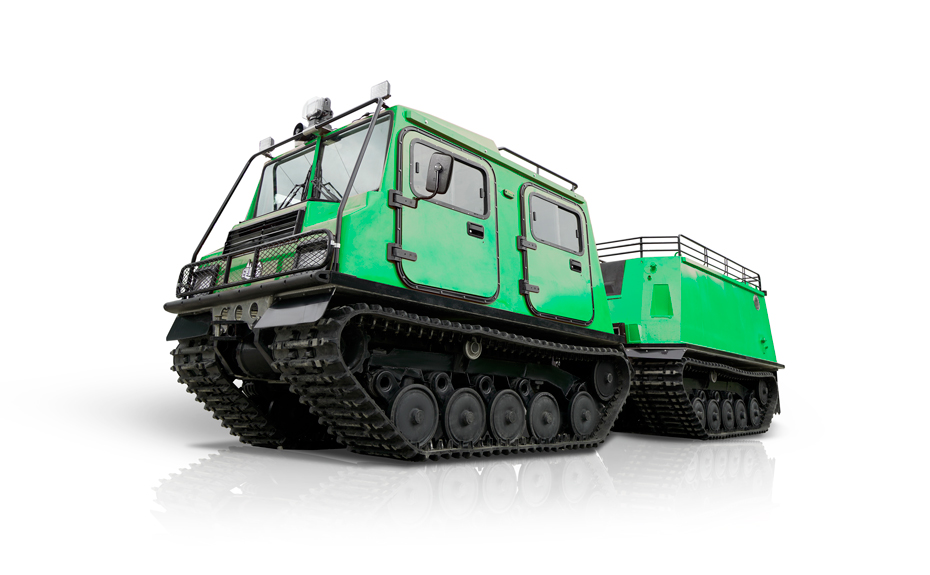
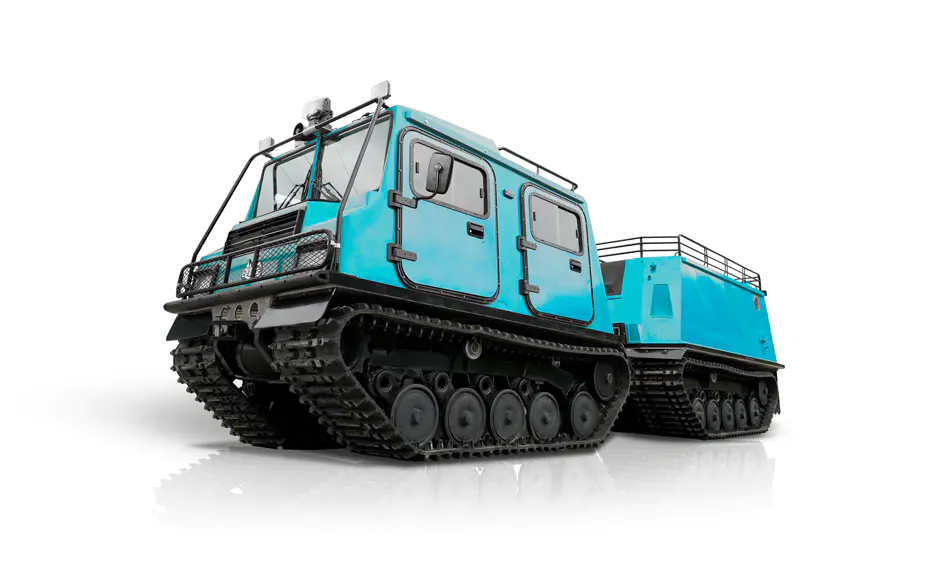
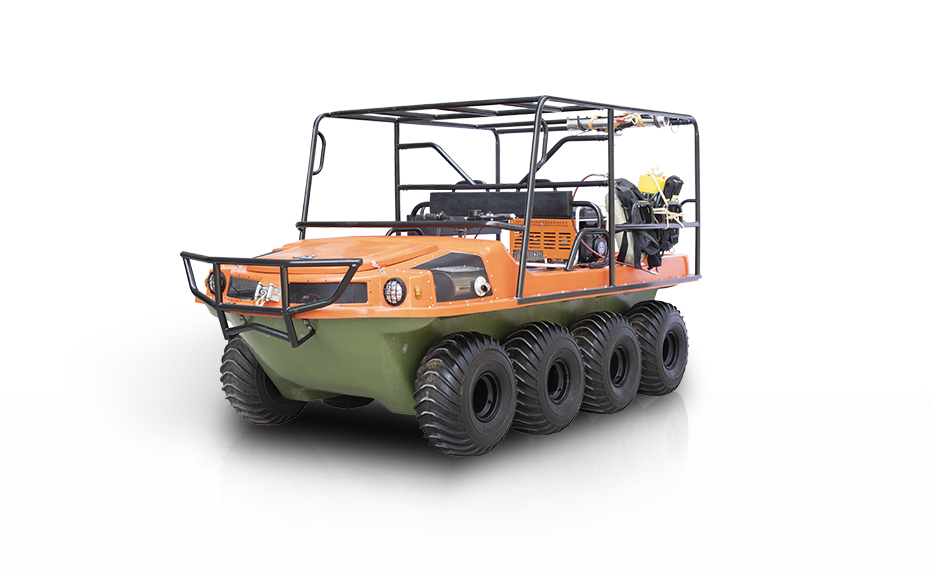
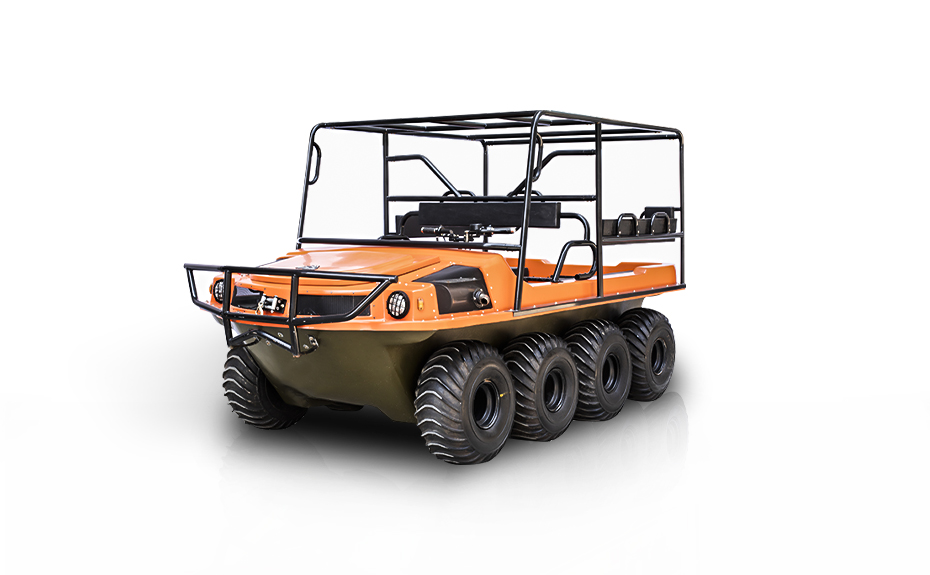
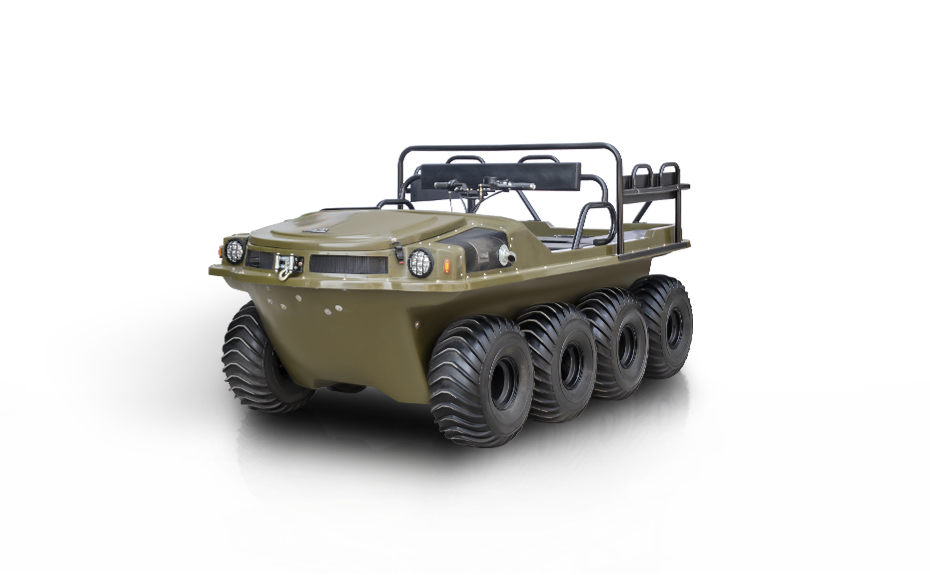
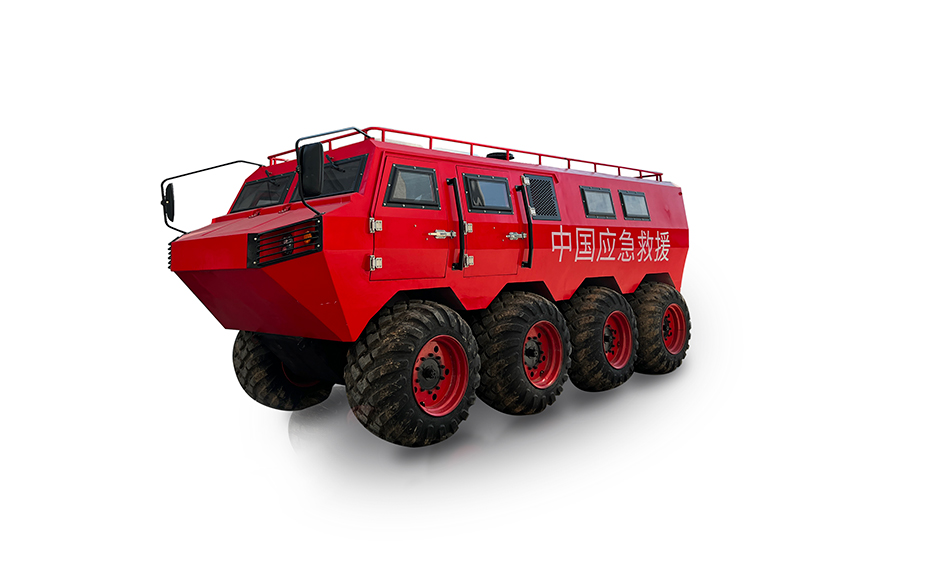
LINHAI HAISDER MACHINERY CO., LTD. presents its Tracked Utility Terrain Vehicle, engineered for predominant performance in challenging and variable terrains. Featuring a durable tracked system, this vehicle delivers enhanced stability, traction, and low ground pressure, enabling safe and efficient operation in environments such as snow, mud, wetlands, and uneven landscapes. Designed for versatility, it supports a range of utility applications including agricultural transport, forestry work, and logistical support. With a robust chassis and reliable powertrain, this tracked vehicle ensures dependable service under demanding conditions. It provides operators with a capable and adaptable solution for off-road tasks requiring consistent mobility and load-bearing capacity.













 浙ICP备2022029871号
浙ICP备2022029871号